The fifth century B.C. was a significant period in ancient Greek history and witnessed a vibrant intellectual and cultural milieu that greatly influenced the development of Greek philosophy. This era, often referred to as the Golden Age of Greece, saw the rise of city-states, including Athens, which became a center of intellectual and artistic achievements. It was a time of political and social upheaval, marked by the Persian Wars, the establishment of democracy in Athens, and the Peloponnesian War. These tumultuous events created a fertile ground for philosophical inquiry, with thinkers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle emerging to explore fundamental questions about knowledge, ethics, and the nature of reality.
However, before Socrates and his successors would come to revolutionize Greek thought – and the fundamental trajectory of Western Civilization – several Pre-Socratic philosophers would contribute key ideas that would shape Greek philosophical discourse. One of these was Empedocles.
Empedocles was philosopher and scientist who lived during the fifth century B.C. Born in Agrigentum, a Greek colony in Sicily, Empedocles made significant contributions to the fields of philosophy, physics, and medicine. He is widely recognized for his influential theories on the nature of reality and the composition of the universe.
Empedocles’ Contributions to Philosophy
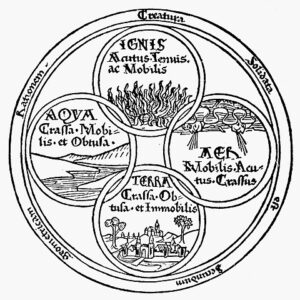
Empedocles proposed a doctrine known as the “four elements,” which postulated that all matter is composed of four fundamental elements: earth, air, fire, and water. According to his theory, these elements were in a constant state of flux and combined in different proportions to give rise to the diverse phenomena observed in the world. He further suggested that love and strife, or attraction and repulsion, were the driving forces behind the combination and separation of these elements. Empedocles’ ideas laid the foundation for later theories of matter and influenced the works of renowned philosophers, including Aristotle.
Another significant contribution of Empedocles was his belief in the transmigration of souls. He believed that the soul was immortal and could, after death, be reborn in another body. This idea influenced many philosophers, including Plato and Aristotle.
In addition to his contributions to philosophy, Empedocles also made significant strides in the fields of biology and medicine. He was one of the first to propose the concept of natural selection and the survival of the fittest in the context of evolution. Empedocles believed that living organisms evolved through a process of trial and error, with those best adapted to their environment surviving and passing on their traits to future generations. His ideas foreshadowed later developments in evolutionary theory and had a lasting impact on the scientific community.
The Legacy of Empedocles
Empedocles’ ideas continue to inspire philosophers, scientists, and thinkers to this day. His belief in the four elements and the two primary forces in the universe has influenced fields as diverse as chemistry, physics, and even psychology. His idea of the transmigration of souls has also inspired many religious and spiritual beliefs.
Empedocles’ theories on health and medicine have also had a lasting impact. His belief in the balance of the four elements within the body has influenced traditional medicine practices such as Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine.
In conclusion, Empedocles was a significant Pre-Socratic thinker whose ideas continue to influence and inspire us today. His legacy serves as a reminder of the enduring impact that philosophical and scientific inquiry can have on our understanding of the universe.


